Diffusion
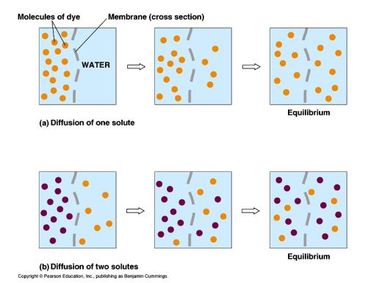
Diffusion: is the net movement of particles (atoms, Ions or molecules) from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration (down a concentration gradient). The rate of diffusion is increase by:
• Higher concentration gradient
• Higher temperature
• Lighter particles
• Higher concentration gradient
• Higher temperature
• Lighter particles
- The difference in concentration of a solute between two regions in a fluid is known as the concentration gradient.
- Diffusion occurs in both liquid eg. Coffee crystal and gas eg. perfume.
- A membrane is not required (although sometimes a fully permeable membrane was used to isolate large molecules in the same fluid eg. cells’ membrane limit larger molecules to pass through such as starch or protein while allowing smaller molecules such as gases and glucose to diffuse across.
- The different types of particles diffuse independently of each other.
Osmosis
Osmosis: is the movement of water molecules from a solution of higher water potential to a solution of lower water potential through a partially permeable membrane.
- Water potential is a measure of tendency of water to move from one place to another. A solution with lower concentration has higher water potential.
- Isotonic=same water potential,
- Hypertonic=lower water potential,
- Hypotonic=higher water potential.
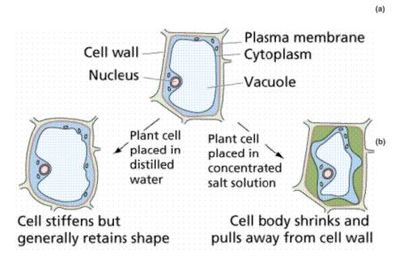
Turgidity: Placing living cells in a solution with higher water potential than the cell’s fluid, water enter the cells. For plant cell, the presence of rigid cell walls prevent bursting of the cell, water enters the cell causing it to expand, it become turgid. For animal cells, there are no cell walls thus the cells will eventually burst.
Plasmolysis: Placing plant cells in a solution with lower water potential than the cell’s fluid, water leave the cells causing shrinkage of the cytoplasm and cell membrane away from the cell wall.
Crenation: Placing animal cells in a solution with lower water potential than the cell’s fluid, water leave the cells causing shrinkage of the cells and little spikes appear on the cell surface membrane. The cells are dehydrated and die eventually.
Plasmolysis: Placing plant cells in a solution with lower water potential than the cell’s fluid, water leave the cells causing shrinkage of the cytoplasm and cell membrane away from the cell wall.
Crenation: Placing animal cells in a solution with lower water potential than the cell’s fluid, water leave the cells causing shrinkage of the cells and little spikes appear on the cell surface membrane. The cells are dehydrated and die eventually.
Active Transport
Active Transport: is the movement of substances against a concentration gradient. Respiration energy is needed.
- Down a concentration gradient: smaller molecules diffuse by passive transport, only large molecules need active transport
- Up a concentration gradient: both large and small molecules needed to use active transport:
- Dissolved mineral salts by root hairs
- Glucose and Amino acids by small intestine of human.
Surface area to volume ratio
- Living organisms are made up of many small cells to increase the cells membrane surface area to volume ratio to increase rate of diffusion & osmosis.
- Cells responsible for absorption of nutrient are modified to maximize the surface area to volume ratio:
- • Red blood cells have flattened and biconcave shape.
- • Root hair cells have long protrusion.
- • Small intestine epithelial cells have microvilli.