Seven Types of English Comprehension Questions
What types of questions can you expect in your English Language Comprehension paper? My analysis of past years’ ‘O’ Level papers suggests that the questions can be generally categorised into seven types:
- The Factual Question
- The Inferential Question
- The Use Your Own Words Question
- The Language Use Question
- Writing down/Quoting a Word/Phrase/Sentence/Expression
- The Vocabulary Question
- The Summary Question
The Factual Question
The word factual’ comes from the word “FACT’, and as the word suggests, this type of question requires you to retrieve facts given in the passage.
Examples of factual questions:
For this type of question, DO NOT INCLUDE FACTS WHICH ARE NOT GIVEN IN THE PASSAGE.
Examples of factual questions:
- who, what, where,when,why and how questions
For this type of question, DO NOT INCLUDE FACTS WHICH ARE NOT GIVEN IN THE PASSAGE.
- The “Who”, ”‘Where” “when”, “Why”, ”How“ and “What“ Questions
More about the ‘Why’ Question
You can begin your answer this way :’Because …’, or if you are uncomfortable with this structure, you can begin this way :’This was because …’. Alternatively, you can just write down the reason.
You can begin your answer this way :’Because …’, or if you are uncomfortable with this structure, you can begin this way :’This was because …’. Alternatively, you can just write down the reason.
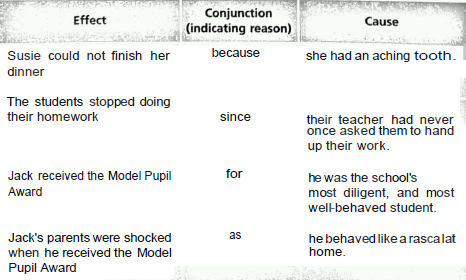
In the English language, there are some signals for indicating the Cause and Effect relationship between events, and these provide important clues for your answer.
In the table below, the sentences have this structure:
In the table below, the sentences have this structure:
Now read the sentences in the table below and answer the questions. Two examples are provided.
Examples
Question 1: Why was Susie unable to finish her dinner?
Answer: This was because she had an aching tooth.
Question 2: Why did the students stop doing their homework?
Answer: Because their teacher had never once asked them to hand up their work.
Question 3: Why was Jack given the Model Pupil Award?
Answer:
Question 4: Why were Jack’s parents shocked when he received the Model Pupil Award?
Answer:
In the following table, the first sentence gives the Cause, and the second sentence begins with a word/phrase that introduces the Effect. Read the sentences in the table below and answer the questions that follow. One example is provided.
Question 1: Why was Susie unable to finish her dinner?
Answer: This was because she had an aching tooth.
Question 2: Why did the students stop doing their homework?
Answer: Because their teacher had never once asked them to hand up their work.
Question 3: Why was Jack given the Model Pupil Award?
Answer:
Question 4: Why were Jack’s parents shocked when he received the Model Pupil Award?
Answer:
In the following table, the first sentence gives the Cause, and the second sentence begins with a word/phrase that introduces the Effect. Read the sentences in the table below and answer the questions that follow. One example is provided.
Question 5: Why did Michael’s neighbours report him to the police?
Answer: Because he stole their bicycles.
Question 6: Why did John fall off the ladder?
Answer:
Answer: Because he stole their bicycles.
Question 6: Why did John fall off the ladder?
Answer:
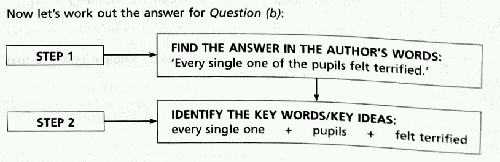
Question (a): Why did the pupils stop to rest? Use your own words in your answer.[2]
Question (b): Using your own words in your answer, explain how the pupils reacted to the sight of a pride of lions marching towards them. [3]
Question (b): Using your own words in your answer, explain how the pupils reacted to the sight of a pride of lions marching towards them. [3]
You do not have to look for points for your answer as the question only requires you to analyse the author’s use of language. So, you can skip Step 1.
But you CAN go back to the context of the expression (perhaps the sentence it’s a part of, or the sentences around it to help you guess the meaning of the expression .
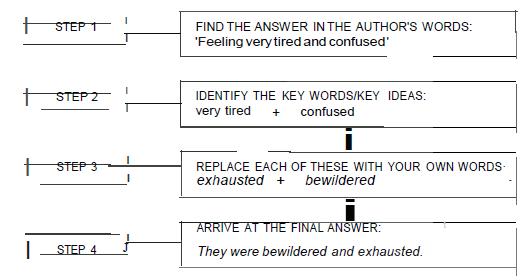
In short, here are the steps to take for answering Use Your Own Words Questions Type II:
STEP 1 : Check the context of the expression.
STEP 2 : Identify key words/key ideas (which may be expressed in two or more words} used by the author.
STEP 3 : Replace each key word/key idea with:
(i} a synonym (a word with similar meaning)
(ii} a phrase with similar meaning
(iii} an associated word
(iv} an antonym* (a word with opposite meaning}
*[Please note that antonyms can only be used in special cases.)
STEP 4 : String your substitute words into a complete sentence that answers the question.
But you CAN go back to the context of the expression (perhaps the sentence it’s a part of, or the sentences around it to help you guess the meaning of the expression .
In short, here are the steps to take for answering Use Your Own Words Questions Type II:
STEP 1 : Check the context of the expression.
STEP 2 : Identify key words/key ideas (which may be expressed in two or more words} used by the author.
STEP 3 : Replace each key word/key idea with:
(i} a synonym (a word with similar meaning)
(ii} a phrase with similar meaning
(iii} an associated word
(iv} an antonym* (a word with opposite meaning}
*[Please note that antonyms can only be used in special cases.)
STEP 4 : String your substitute words into a complete sentence that answers the question.
For this question, we can use word association to come up with the replacements for each key word/key idea.
(i) ‘walking.
What do we associate with talking’?
Answer: Legs
And we associate legs with_______ ?
Answer: People
Now since the expression in question refers to Jear’s son, the replacement should be in the singular form: *person,.
So, voila\ You,ve got your replacement for ‘walking,!
(ii) ‘dictionary.
What is a dictionary?
Answer: It is a book that provides the meanings of most, if not all, of the words in a certain language.
And since the expression ‘walking dictionary* refers to Jean’s son, it suggests that he must know the meanings of not necessarily all the words in the language but probably a lot more words than the average person does…………..
(i) ‘walking.
What do we associate with talking’?
Answer: Legs
And we associate legs with_______ ?
Answer: People
Now since the expression in question refers to Jear’s son, the replacement should be in the singular form: *person,.
So, voila\ You,ve got your replacement for ‘walking,!
(ii) ‘dictionary.
What is a dictionary?
Answer: It is a book that provides the meanings of most, if not all, of the words in a certain language.
And since the expression ‘walking dictionary* refers to Jean’s son, it suggests that he must know the meanings of not necessarily all the words in the language but probably a lot more words than the average person does…………..